| Figure 4 |
 |
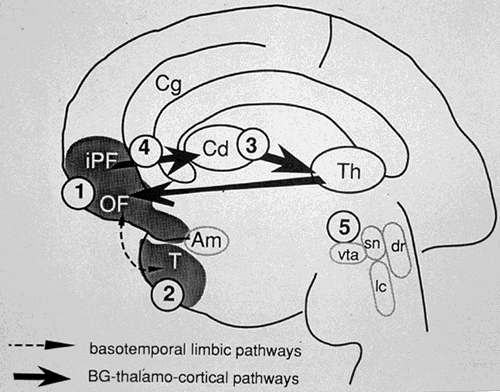
| Possible mechanisms for common dysfunction of basotemporal limbic cortex in depression with three basal ganglia (BG) diseases, showing primary cell loss in frontal cortex; 1), remote changes in basotemporal limbic regions; 2), anterograde or retrograde disruption of BG-thalamo-cortical circuits from caudate degeneration or injury; 3,4), and degeneration of mesencephalic monoamine neurons and their cortical projections; 5), Note: Am = amygdala; Cd = caudate; Cg = anterior cingulate; dr = dorsal raphe; iPF = inferior prefrontal cortex; lc = locus coeruleus; OF = orbital frontal cortex; sn = substantia nigra; T = temporal cortex; Th = thalamus; vta = ventral tegmental area. With permission from Mayberg et al. 1992 (57). |
| Back to Chapter |
published 2000