| FIG. 5 |
 |
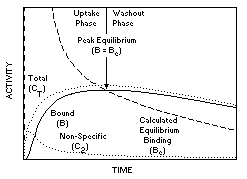
| A diagram of the kinetics of regional brain activity for a radioligand over time, including curves depicting the concentrations of total regional (CT), free and nonspecifically bound (C2), and specifically bound (B) activities. The calculated equilibrium binding (Be) is defined as the concentration of bound that satisfies the Michaelis-Menten equation: Be = (Bmax{ewc MVIMG, MVIMAGE,!dot.bmp}Free)/(KD + Free), where Free = C2 * f2 and f2 is the fraction of free tracer in the compartment. During the initial phase following a bolus injection of tracer, B < Be, so association is greater than dissociation, and the activity in the brain increases (uptake phase). At the point in time when specific binding (B) peaks (arrow), B = Be, association is equal to dissociation, and equilibrium conditions are satisfied. Because free tracer concentrations will fall as a result of peripheral clearance from the plasma, immediately after peak, B > Be, dissociation is greater than association, and brain activity decreases (washout phase). The time to reach equilibrium varies and depends upon blood flow, brain extraction, receptor affinity and density, and peripheral clearance. When equilibrium is not achieved during the time-frame of the experiment, only the uptake phase is observed, and the ligand's binding is said to be irreversible. |
| Back to Chapter |
published 2000