| Figure 2 |
 |
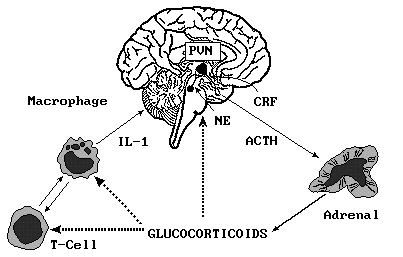
| A schematic diagram of the relationship between the brain, the HPA axis, and immune cells. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) produced by lymphocytes during the immune response activates noradrenergic (NE) projections for the brainstem to the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN). This input activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis, stimulating the release of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the median eminence region of the hypothalamus, which in turn stimulates the secretion of ACTH from the anterior lobe of the pituitary, which then activates the adrenal cortex to synthesize and secrete glucocorticoid hormones. The glucocorticoids in turn provide a negative feedback on cytokine production by lymphocytes. |
| Back to Chapter |
published 2000